Биндгеймит
Биндгеймит(англ. BINDHEIMITE) - 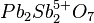
| Типичные примеси |
As,Bi,Ca,Fe,Na |
|---|
| Молекулярный вес |
770.15 |
|---|
| Происхождение названия |
По German chemist, Johann J. Bindheim (1750-1825) who first analysed the mineral. |
|---|
| IMA статус |
действителен, описан впервые до 1959 (до IMA) |
|---|
| Год открытия |
1800 |
|---|
КЛАССИФИКАЦИЯ
| Strunz (8-ое издание) |
4/C.11-70 |
|---|
| Dana (8-ое издание) |
44.1.1.2 |
|---|
| Hey's CIM Ref. |
24.3.5 |
|---|
ФИЗИЧЕСКИЕ СВОЙСТВА
| Цвет минерала |
желтый, желто-коричневый, коричневый, белый, серый, зеленоватый; бесцветный переходящий в желтый и, а коричневый во внутренних рефлексах и напросвет |
|---|
| Цвет черты |
белый, желтовато- белый |
|---|
| Прозрачность |
полупрозрачный, непрозрачный |
|---|
| Блеск |
смоляной, тусклый, матовый |
|---|
| Твердость (шкала Мооса) |
4 - 4.5 |
|---|
| Излом |
раковистый |
|---|
| Плотность (измеренная) |
4.6 - 8.4 g/cm3 |
|---|
| Плотность (расчетная) |
6.8 g/cm3 |
|---|
| Радиоактивность (GRapi) |
0 |
|---|
ОПТИЧЕСКИЕ СВОЙСТВА
КРИСТАЛЛОГРАФИЧЕСКИЕ СВОЙСТВА
Перевод на другие языки
 немецкий — Antimonbleispath;Antimonsaures Bleioxyd;Bindheimit;Bleiniere;Blumit (of Fischer) немецкий — Antimonbleispath;Antimonsaures Bleioxyd;Bindheimit;Bleiniere;Blumit (of Fischer)
 русский — Биндгеймит русский — Биндгеймит
|
 испанский — Bindheimita испанский — Bindheimita
 английский — Bindheimite английский — Bindheimite
|
|
Ссылки
Список литературы
- Bindheim (1792) Schriften der Gesellschaft naturforschender Freunde in Berlin, Schr.: 10: 374.
- Karsten, D.L.G. (1800) Mineralogische Tabellen, Berlin. First edition: 77 (as Bleiniere).
- Glocker, E.F. (1847) Generum et specierum mineralien secundum ordines naturals digestorum synopsis. Halle: 257 (as Stibiogalenites).
- Nicol, J (1849) Manual of Mineralogy, Edinburgh: 319 (as Bleinierite).
- Leymérie, A.F.G.A. (1859) Cours de minéraogie. Toulouse. Third edition, 2 volumes: 2: 283 (as Moffrasite).
- Fischer (1863) Neues Jahrbuch für Mineralogie, Geologie und бледноontologie, Heidelberg, Stuttgart: 559 (as Blumit).
- Dana, J.D. (1868) System of Mineralogy, 5th. Edition, New York: 591.
- Adam, M. (1869) Tableau minéralogique, Paris: 37 (as Pfaffite).
- Prior and Spencer (1895) Mineralogical Magazine: 11: 23.
- Lacroix, A. (1910) Minéralogie de la France et des ses colonies, Paris. 5 volumes: vol. 4: 514.
- Knopf (1918) U.S. Geological Survey Bulletin 660: 249.
- Shannon, Earl V. (1920) Economic geology: 15: 88.
- Larsen, E.S. (1921) The Microscopic Determination of the Nonнепрозрачный Minerals, First edition, USGS Bulletin 679: 47.
- Shannon, Earl V. (1926) “The Minerals of Idaho,” U.S. National Museum Bulletin 131: 438.
- Hintze, Carl (1931) Handbuch der Mineralogie. Berlin and Leipzig. 6 volumes: 1 [4B]: 838.
- Natta and Baccaredda (1933) Zeitschrift für Kristallographie, Mineralogie und Petrographie, Leipzig: 85: 271.
- Hägele (1937) Centralblatt für Mineralogie, Geologie und бледноontologie, Stuttgart: 45.
- Meixner (1937) Centralblatt für Mineralogie, Geologie und бледноontologie, Stuttgart: 38.
- Le Mesurier (1939) Journal of the Royal Society of Western Australia: 25: 137.
- Palache, C., Berman, H., & Frondel, C. (1951), The System of Mineralogy of James Dwight Dana and Edward Salisbury Dana, Yale University 1837-1892, Volume II. John Wiley and Sons, Inc., New York, 7th edition, revised and enlarged, 1124 pp.: 1018-1020.
- Mason, B. and Vitaliano, C. J. (1953): The mineralogy of the antimony oxides and antimonates. Mineralogical Magazine 30, 100-112.
- Bothwell, D. I., Davis, R. J. and Moss, A. A. (1960): A bismuth-bearing variety of bindheimite. Mineralogical Magazine 32, 664-666.
- Anthony, J.W., Bideaux, R.A., Bladh, K.W., and Nichols, M.C. (1997) Handbook of Mineralogy, Volume III. Halides, Hydroxides, Oxides. Mineral Data Publishing, Tucson, AZ, 628pp.: 57.
|